How Do You Know if Something Is a Diastomer
iv.iii Diastereomers
- Folio ID
- 14998
Diastereomers are stereoisomers that are not related every bit object and mirror image and are not enantiomers. Dissimilar enatiomers which are mirror images of each other and non-sumperimposable, diastereomers are not mirror images of each other and not-superimposable. Diastereomers tin can accept different physical properties and reactivity. They have unlike melting points and humid points and unlike densities. They have two or more than stereocenters.
Introduction
It is like shooting fish in a barrel to mistake betwixt diasteromers and enantiomers. For example, we have 4 steroisomers of 3-bromo-2-butanol. The iv possible combination are SS, RR, SR and RS (Figure ane). One of the molecule is the enantiomer of its mirror prototype molecule and diasteromer of each of the other two molecule (SS is enantiomer of RR and diasteromer of RS and SR). SS's mirror image is RR and they are not superimposable, so they are enantiomers. RS and SR are non mirror paradigm of SS and are not superimposable to each other, so they are diasteromers.
.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=720&height=519)
Figure one
Diastereomers vs. Enantiomers vs. Meso Compounds
Tartaric acid, C4H6Ovi , is an organic compound that can be found in grape, bananas, and in vino. The structures of tartaric acid itself is actually interesting. Naturally, it is in the course of (R,R) stereocenters. Artificially, it can exist in the meso form (R,Due south), which is achiral. R,R tartaric acid is enantiomer to is mirror epitome which is S,South tartaric acid and diasteromers to meso-tartaric acid (figure 2).
(R,R) and (S,S) tartaric acid have similar physical properties and reactivity. However, meso-tartaric acid have different physical properties and reactivity. For example, melting point of (R,R) & (S,South) tartaric is about 170 degree Celsius, and melting point of meso-tartaric acid is nigh 145 caste Celsius.
.bmp?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=720&height=567)
Figure 2
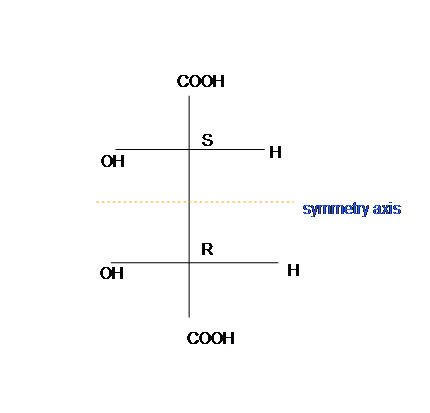
To place meso, meso chemical compound is superimposed on its mirror image, and has an internal airplane that is symmetry (figure 3). Meso-tartaric acid is achiral and optically unactive.
Problems
Place which of the following pair is enantiomers, diastereomers or meso compounds.
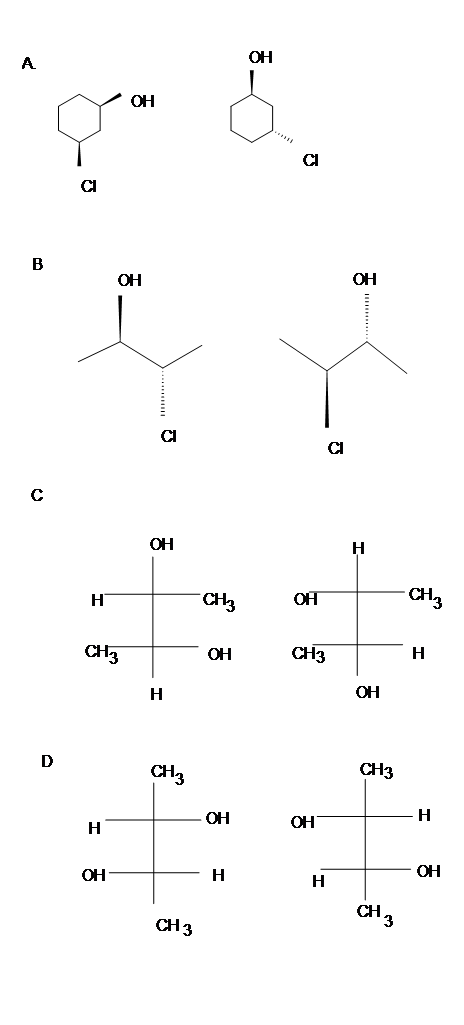
Answer
- Diasteromers
- Identical
- Meso
- Enantiomers
4.3.1 Unlike Types of Isomers
4.three.2 Meso Compounds
Meso compounds are achiral compounds that has multiple chiral centers. It is superimposed on its mirror paradigm and is optically inactive despite its stereocenters.
Introduction
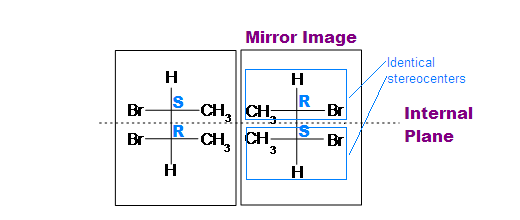
In general, a meso chemical compound should contain 2 or more identical substituted stereocenters. Also, it has an internal symmetry plane that divides the compound in half. These 2 halves reverberate each other by the internal mirror. The stereochemistry of stereocenters should "cancel out". What it means here is that when we take an internal plane that splits the chemical compound into ii symmetrical sides, the stereochemistry of both left and correct side should be contrary to each other, and therefore, result in optically inactive. Cyclic compounds may also be meso.
Identification
If A is a meso chemical compound, it should have 2 or more than stereocenters, an internal plane, and the stereochemistry should exist R and S.
- Look for an internal plane, or internal mirror, that lies in betwixt the compound.
- The stereochemistry (e.g. R or S) is very crucial in determining whether it is a meso compound or non. As mentioned to a higher place, a meso chemical compound is optically inactive, so their stereochemistry should abolish out. For instance, R cancels S out in a meso compound with ii stereocenters.
.bmp?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=375&height=171)
trans-ane,two-dichloro-1,2-ethanediol
.bmp?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=433&height=183)
(meso) -2,3-dibromobutane
Tips: An interesting thing virtually single bonds or sp3-orbitals is that nosotros can rotate the substituted groups that fastened to a stereocenter effectually to recognize the internal plane. Equally the molecule is rotated, its stereochemistry does not change. For example:
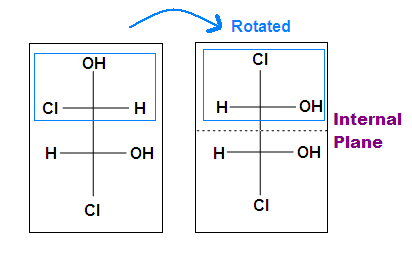.bmp?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=412&height=258)
Another case is when we rotate the whole molecule by 180 degree. Both molecules beneath are still meso.
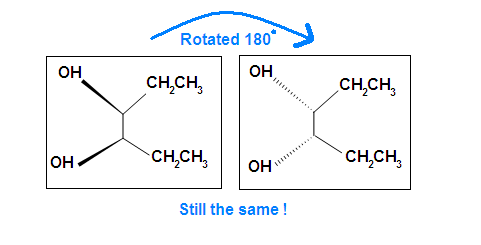
Remember the internal plane here is depicted on ii dimensions. Nonetheless, in reality, it is three dimensions, so be aware of information technology when we place the internal mirror.
Example
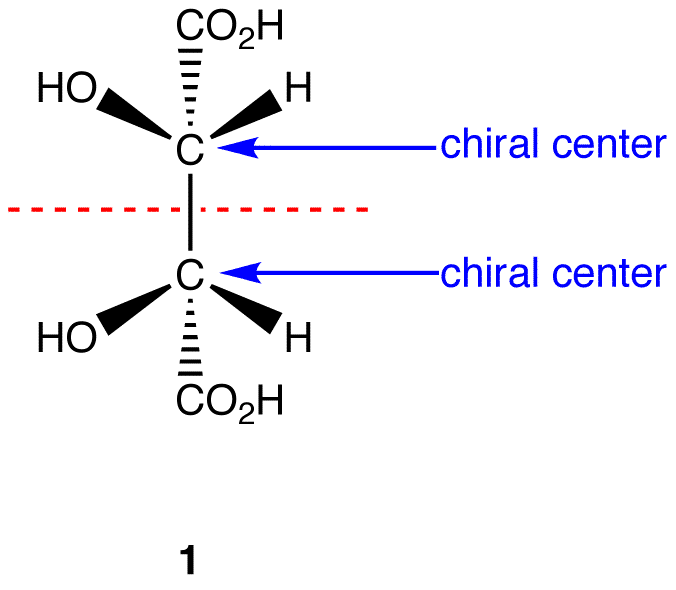
This molecule has a plane of symmetry (the horizontal plane going through the ruby cleaved line) and, therefore, is achiral; Still, it has ii chiral carbons and is consequentially a meso compound.
Case ii
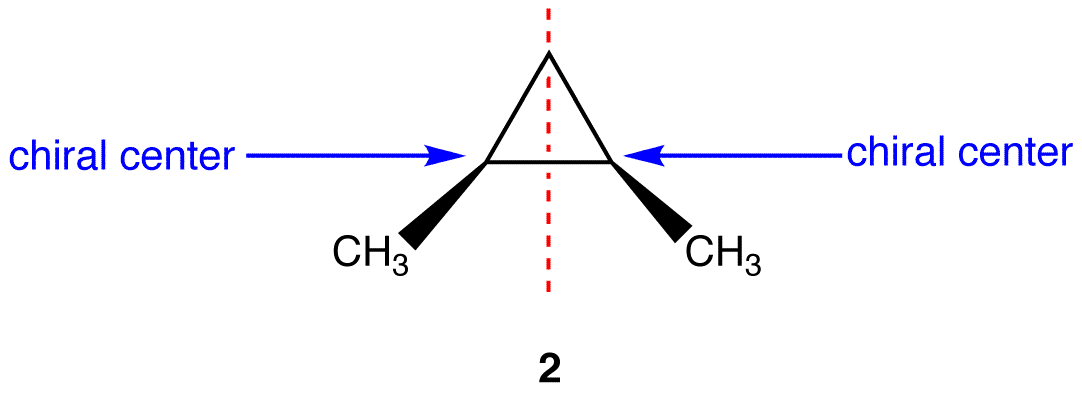
This molecules has a airplane of symmetry (the vertical plane going through the crimson broken line perpendicular to the airplane of the ring) and, therefore, is achiral, merely has has two chiral centers. Thus, its is a meso compound.
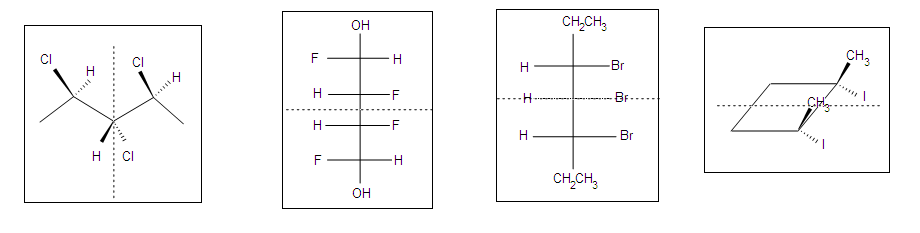
Other Examples of meso compounds
Meso compounds can exist in many different forms such as pentane, butane, heptane, and even cyclobutane. They exercise not necessarily have to be 2 stereocenters, just can accept more.
.bmp?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=695&height=176)
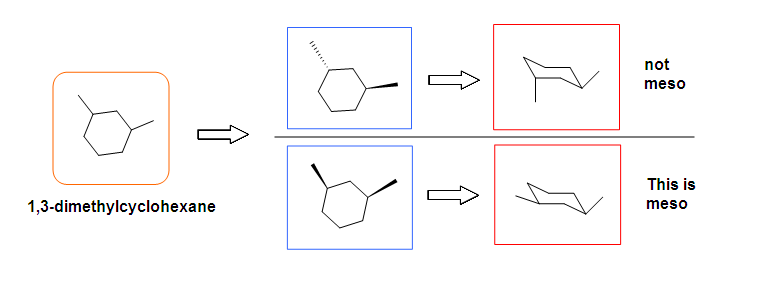
Optical Activeness Analysis
When the optical activity of a meso compound is attempted to be adamant with a polarimeter, the indicator will not prove (+) or (-). It simply means there is no certain direction of rotation of the polarized light, neither levorotatory (-) and dexorotatory (+).
Issues
Abreast meso, there are also other types of molecules: enantiomer, diastereomer, and identical. Determine if the following molecules are meso.
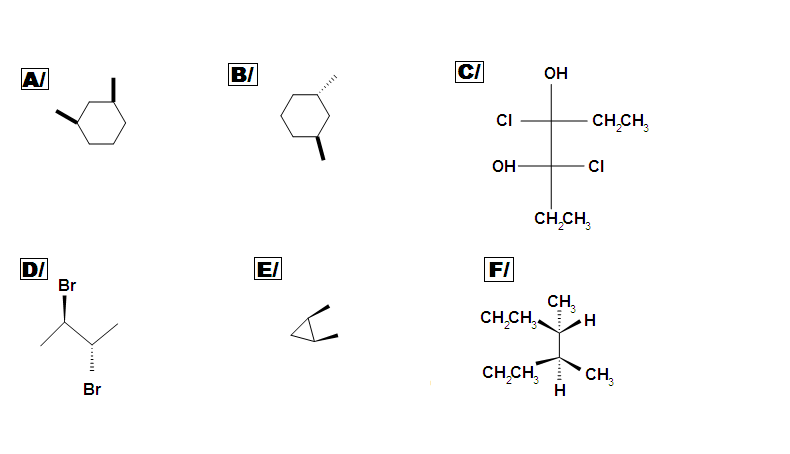
Respond key: A C, D, E are meso compounds.
References
- Vollhardt, One thousand. P.C. & Shore, N. (2007). Organic Chemical science (5thEd.). New York: Due west. H. Freeman. (190-192)
- Shore, N. (2007). Study Guide and Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry (5th Ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman. (seventy-80)
Source: https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Purdue/Purdue_Chem_26100:_Organic_Chemistry_I_%28Wenthold%29/Chapter_04:_Stereochemistry/4.3_Diastereomers
0 Response to "How Do You Know if Something Is a Diastomer"
Post a Comment